How Long Does Registered Mail Take From Hong Kong To Us

Hong Kong has a long history of protestors fighting for autonomy and self-determination, but, under both the United Kingdom and China, Hong Kong and its people accept struggled to become a commonwealth. Currently, Hong Kong is designated as a "special administrative region" of China. In theory, this means a big degree of autonomy from mainland Cathay under the "1 Land, 2 Systems" policy. However, the cardinal phrase here is in theory.
On June xxx, 2020, a new security constabulary has clouded that autonomy: No only is it no longer clear if Hong Kong tin determine its ain policies separate from Beijing, merely the new police gives Red china the power to extradite any Hong Kong citizen with fiddling to no cause. To understand its current crisis with Red china, it's essential to reflect on Hong Kong's complex history — and the style that history continues to reflect in 2021.
British Colonial Rule Overtakes Hong Kong
After the first Opium State of war, Mainland china ceded the isle of Hong Kong to United kingdom of great britain and northern ireland. In 1860 and 1898 respectively, additional territories — known today as the Kowloon Peninsula and the New Territories — were ceded to the British. From then on, the British colonized Hong Kong, enacting racist and white supremacist policies accordingly, including banning the use of the Chinese linguistic communication in government and creating segregated European-but neighborhoods that were subject area to dissimilar laws.
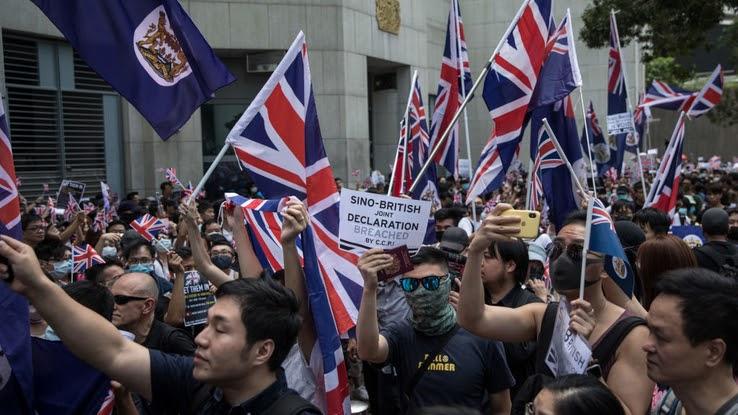

Declassified documents show that pressure from Chinese leaders made information technology articulate that the People's Democracy of China would invade Hong Kong if it attained self-rule. For example, in 1958, Premier Zhou Enlai called whatever endeavour to bring commonwealth to the island "a very unfriendly deed." That is, despite enjoying the benefits of having a wealthy and economically strong neighbour like Hong Kong, Mainland china viewed the prospect of democracy in Hong Kong as a step toward independence rather than reunification with China.
Yet, folks living in Hong Kong pushed for reform and freedom from decades of colonial rule. In the 1960s and '70s, protests over labor conditions somewhen led to a higher standard of living and pressured the colonizers to revoke racist laws. Encouraged past these successes, Hong Kongers exercised their freedom of speech, protested and held communist rallies in the open.
The British "Return" Hong Kong to Communist china
While some Hong Kongers were optimistic almost reunification with China, others, particularly students, worried that China would endeavor to take away Hong Kong's freedoms instead of preserving the "One Country, Two Systems" policy. These fears increased after the 1989 Tiananmen Square massacre — a violent crackdown confronting pro-democracy protests in Prc that caused hundreds or thousands of deaths.
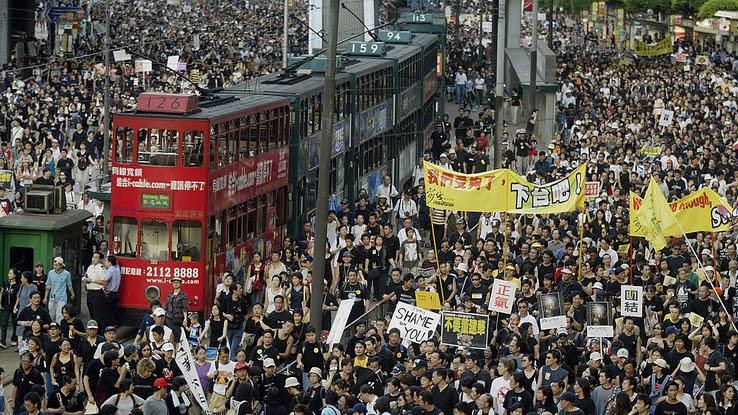

Nonetheless, after more than than a decade of negotiations and preparation, Hong Kong was returned to Red china on July 1st, 1997. Under the deal, Hong Kong was guaranteed autonomy until 2047. During that time, the Basic Law, a miniature constitution agreed upon by Mainland china and the United Kingdom, was to be the police force of the country in Hong Kong.
In 2003, an attempt was made to pass a law that would make secession, sedition, subversion or treason against the Chinese authorities illegal. This triggered the first major protests against the Chinese government, with 500,000 people turning out on July 1 to express their outrage. Ultimately, the legislation was shelved — at to the lowest degree for a time.
Prc's Attempts to Change Education in Hong Kong
In the years that followed the 2003 protests, the Chinese Communist Party (CCP) promised democratic reforms in the time to come. And, although a few alterations were made to Hong Kong'southward legislature, little actually changed — at least, not the management many Hong Kongers hoped.

In 2012, attempts were fabricated to change the curriculum of Hong Kong's schools to focus more than on Chinese history and identity. This was seen by many Hong Kongers as an endeavor to feed younger generations propaganda about mainland China. Massive protests broke out, with secondary schoolhouse students (roughly equivalent to American centre and high schoolers) leading the protest through a grouping called Scholarism. Hong Kong's chief executive at the time announced that implementing the curriculum would be optional, rendering China's educational plan powerless.
The Umbrella Revolution Grips the World
Even though information technology was ultimately unsuccessful, the Umbrella Revolution is peradventure the most iconic of Hong Kong'due south protests. Information technology was sparked by fears that the Chinese government did non intend to go on a promise to create universal suffrage for the metropolis'south executive officer by 2017. Protestors demanded the resignation of the current pro-Beijing executive officeholder and balloter reform, but they had difficulty like-minded on the specifics of the latter demand.
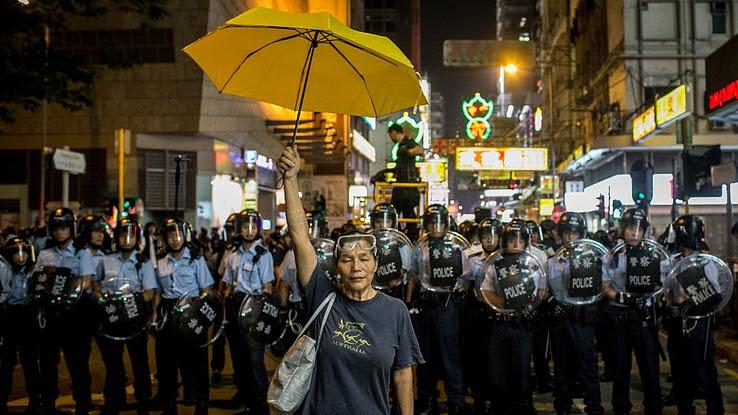
The protests were some of the most vehement and chaotic since the 1960s, with the protestors' use of umbrellas to deflect tear gas canisters giving the movement its name. Additionally, the protestors gained international attending for sharing complimentary food with each other and setting up recycling stations to proceed streets make clean. Somewhen, the protests were done in by an inability to unify around a unmarried gear up of demands and the return of many educatee protestors to school. Nonetheless, the protests permanently strained relations betwixt the people of Hong Kong and mainland china.
Communist china Introduces the Hong Kong Security Law
After the Umbrella Revolution, protests became much more common, with more existence held in response to a crackdown on unlicensed food vendors too as the beginning-ever rally for Hong Kong independence in 2016. In 2019, a new national security constabulary was introduced, one that, if passed, would extradite Hong Kong citizens suspected of criminal activity on the mainland to China without a trial.
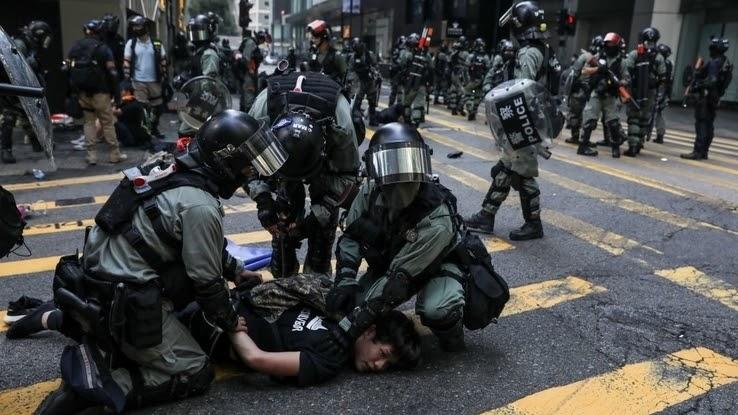

Protests bankrupt out quickly, swelling to massive numbers when Principal Executive Carrie Lam amended the law to also let extradition to Mainland china for criminal charges. In fact, the protests marked the "biggest political crunch in decades" and, according to Reuters, "pose the most serious popular challenge to China's President 11 Jinping since he came to power." Although Carrie Lam appear on June 15, 2019 that the law would be delayed indefinitely, protestors argued that the law could notwithstanding be implemented at whatever time and refused to disperse.
China Makes Protest Most Incommunicable for the People of Hong Kong
From there, the protests became a broader pro-democracy motility. Police force violence against protestors escalated — and constabulary enforcement was suspected of colluding with triad street gangs to attack and intimidate protestors. Eventually, Beijing intervened directly by passing a new security beak. Protestors, the United Kingdom and a myriad of other countries contest the legality of this move, but there'due south little anyone tin can do to oppose the Chinese legislation, which allows for the extradition of Hong Kong citizens to Red china and lifetime prison sentences for those folks charged with secession, subversion, terrorism and bunco.

Additionally, the law also grants Communist china and the Beijing-backed main executive a range of new powers, including wire tapping, closed-door trials, the ability to appoint new judges in national security trials and more. Many kinds of protestation now count as secession, subversion, terrorism or collusion, including devastation of property. The police went into issue merely before July 1, the anniversary of Hong Kong's handover to Mainland china. Since then, police have shutdown any attempted protests — even though protests and rallies are traditionally held on July 1 — and, in addition to making mass arrests, have used tear gas and safe bullets against Hong Kong citizens.
In response, Hong Kongers have begun deleting social media posts and destroying pro-commonwealth signs out of fearfulness of extradition. In endeavour to help Hong Kongers, the Britain promised a path to citizenship for 3 million Hong Kongers — and Taiwan, Australia and the The states accept also made moves to assistance people from the city who may soon need to seek political asylum. Whether this severe turn of events marks the end of the fight for self determination in Hong Kong or not, it'south clear that the new constabulary has irrevocably upended life for the people of Hong Kong.
How Long Does Registered Mail Take From Hong Kong To Us,
Source: https://www.reference.com/history/hong-kong-relationship-china-c6dcc7ea8a2fabdc?utm_content=params%3Ao%3D740005%26ad%3DdirN%26qo%3DserpIndex
Posted by: heitmannhation1977.blogspot.com


0 Response to "How Long Does Registered Mail Take From Hong Kong To Us"
Post a Comment